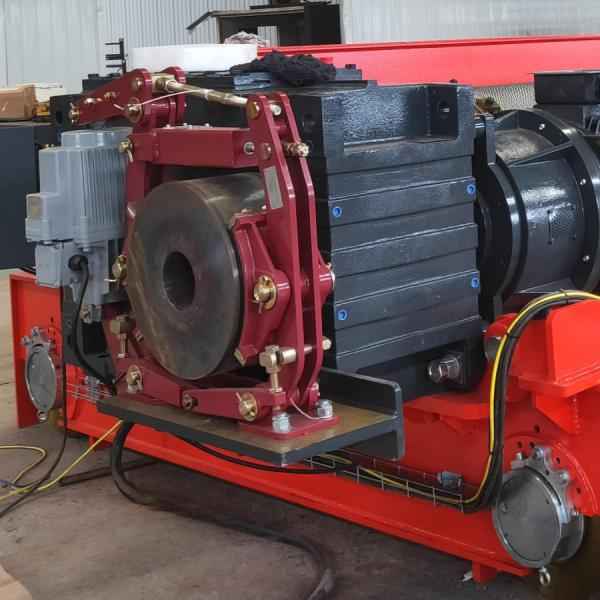
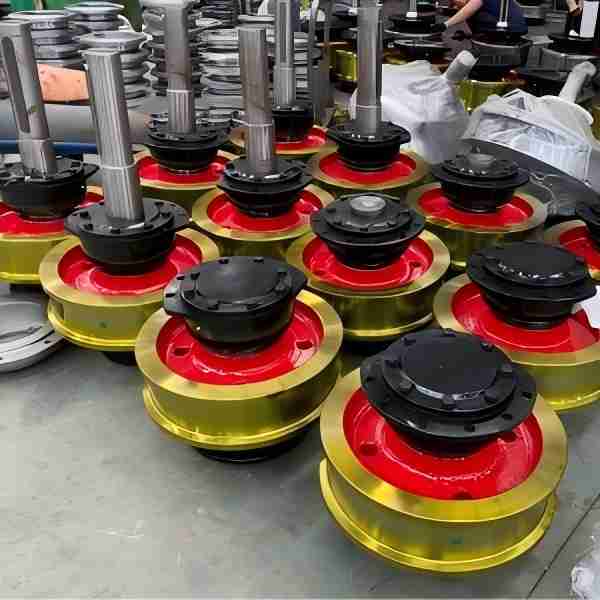
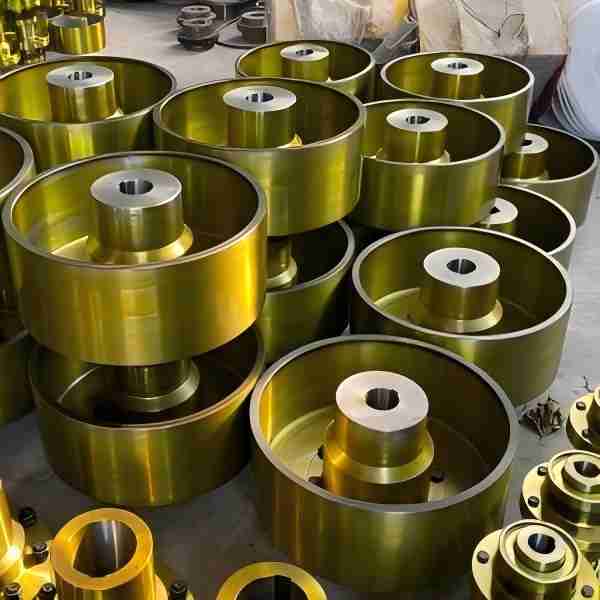
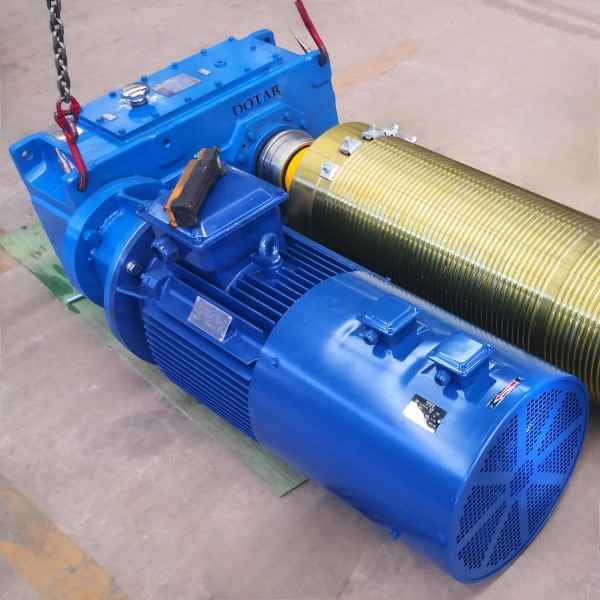
In the field of heavy machinery and material handling, crane gear couplings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operations. These mechanical components efficiently transmit torque while compensating for misalignment between connected shafts. Since precision, durability, and flexibility are vital for safe and effective crane operations, gear couplings have become indispensable in modern lifting systems.
Basic Concept of Gear Couplings
A gear coupling is a type of flexible coupling consisting of two hubs with external teeth and a sleeve with internal teeth. These components mesh together, allowing the coupling to accommodate misalignment, reduce vibrations, and transmit torque efficiently. Typically made of high-strength materials such as alloy steel, gear couplings are designed to withstand heavy loads and harsh operating conditions.
Importance of Gear Couplings in Cranes
During operation, cranes are subjected to dynamic loads, impact forces, and varying working conditions. Therefore, gear couplings serve several critical functions:
- Efficient Torque Transmission – Gear couplings ensure smooth torque transfer from the motor to the hoisting or travel mechanism.
- Misalignment Compensation – Due to structural deformation or thermal expansion, cranes may experience shaft misalignment. Gear couplings effectively compensate for angular and parallel misalignments.
- Shock Absorption – Sudden starts, stops, or load changes can generate impact loads, which may damage other components. Gear couplings absorb these shocks, thereby extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs – With proper lubrication and maintenance, gear couplings can operate for extended periods, reducing downtime and operational expenses.
Types of Crane Gear Coupling
Depending on the specific application, cranes utilize different types of gear couplings, including:
- Flexible Gear Couplings – The most common type, providing excellent torque transmission along with flexibility to accommodate misalignment.
- Rigid Gear Couplings – Suitable for applications requiring high alignment precision, such as motor-to-gearbox shaft connections.
- Floating Shaft Gear Couplings – Used for long-span shaft connections, such as bridge cranes, where greater misalignment must be accommodated.
- Half Gear Couplings – Consisting of a gear hub and a rigid sleeve, these are ideal for applications with limited space or specific alignment requirements.
Selection Criteria for Crane Gear Coupling
Selecting the right crane gear coupling requires considering several critical factors to ensure optimal performance:
- Rated Torque – The coupling must meet the crane’s maximum working torque requirements and provide an adequate safety margin.
- Misalignment Compensation – It should accommodate angular, axial, and radial misalignment under specific working conditions.
- Load Capacity – The coupling must withstand the crane’s maximum load and operating conditions to ensure long-term stability.
- Material and Surface Treatment – High-strength alloy steel with wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coatings enhances durability in harsh environments.
- Lubrication Requirements – Choosing a coupling with an appropriate lubrication system, such as oil or grease lubrication, helps minimize wear.
- Environmental Adaptability – Factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosion resistance should be considered.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance – Selecting a coupling that is easy to install and disassemble can reduce maintenance time and improve operational efficiency.
Maintenance and Lubrication of Gear Coupling
To maximize the lifespan of crane gear couplings, regular maintenance is essential. The following key measures help ensure reliable performance:
- Regular Lubrication – Using high-quality grease or oil reduces wear and enhances efficiency.
- Alignment Inspection – Ensuring proper alignment minimizes unnecessary stress and prolongs service life.
- Wear Inspection – Conducting routine visual and operational checks helps detect early signs of wear or damage.
- Bolt and Fastener Inspection – Loose bolts can cause misalignment and coupling failure, so regular tightening checks are necessary.
Conclusion
Crane gear couplings are indispensable components in material handling and lifting operations. Their ability to efficiently transmit torque, compensate for misalignment, and absorb shocks makes them an ideal choice for cranes in industrial and construction environments. By selecting the right gear coupling and following proper maintenance practices, businesses can enhance the efficiency, safety, and longevity of their crane systems. Ultimately, investing in high-quality gear couplings improves operational performance and reduces downtime, making them a critical part of crane design and functionality.