Introduction to Forged Crane Wheel
Forged crane wheels play a crucial role in the operation of cranes. These wheels are widely used in overhead cranes, gantry cranes, and port cranes. Their primary function is to support the crane’s weight and roll along the track, enabling movement and material transportation. Since crane wheels endure high loads and frequent friction, the quality of the forging process directly impacts their lifespan and operational efficiency.
Advantages of Forged Crane Wheels
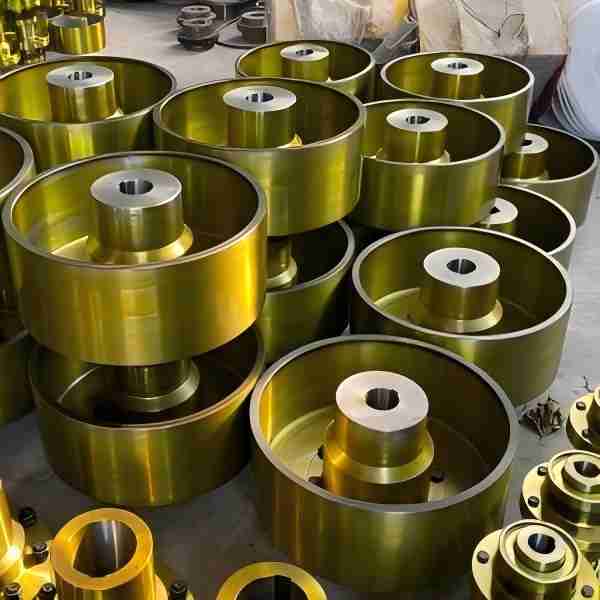
- High Strength and Wear Resistance: Manufacturers use high-strength alloy steel to produce forged crane wheels. Through heat treatment and quenching processes, they significantly enhance the hardness and wear resistance of these wheels.
- Impact and Fatigue Resistance: The forging process increases the internal density of the material, reducing pores and impurities. As a result, the wheels gain superior impact resistance and enjoy an extended service life.
- Precision Machining: During production, forged wheels undergo precise CNC machining. This ensures high accuracy in tread, rim, and bore dimensions, leading to stable operation and minimizing rail gnawing and uneven wear.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: In humid or highly corrosive environments, forged wheels receive specialized anti-corrosion treatments, such as surface coating or galvanization, to prolong their lifespan.
Common Issues and Solutions for Crane Wheels
- Wheel Wear: Continuous operation gradually wears down the wheel tread, affecting stability. Regularly inspecting and repairing or replacing the tread effectively addresses this issue.
- Rim Cracks or Deformation: Overloading or improper rail alignment can cause rim cracks or deformation. Strictly controlling the load and ensuring correct track installation and maintenance can prevent these problems.
- Rail Gnawing: When wheels and rails are misaligned, excessive friction occurs between them. Adjusting wheel spacing and maintaining straight rails can significantly reduce this issue.
- Bearing Failure: Inadequate lubrication or prolonged exposure to excessive loads can lead to bearing failure. Regularly checking lubrication levels and replacing damaged bearings ensures smooth operation.
Maintenance and Care for Crane Wheel
To ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of forged crane wheels, operators should follow these maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspections: Frequently examine the wheel tread, rim, bearings, and connecting components. Address any abnormalities promptly.
- Proper Lubrication: Regularly apply lubricant to the wheel bearings to minimize friction and enhance efficiency.
- Track Alignment Adjustments: Maintaining track straightness prevents uneven wear and eliminates rail gnawing.
- Load Management: Avoiding prolonged overloading reduces fatigue damage to the wheels and associated components.
Conclusion
Forged crane wheels are essential for crane operations, as their quality and performance directly influence stability and safety. A well-designed, correctly installed, and properly maintained wheel system can significantly extend service life, lower maintenance costs, and improve productivity. Therefore, when selecting and using forged crane wheels, it is crucial to consider material composition, manufacturing processes, and working conditions to ensure efficient crane operations.