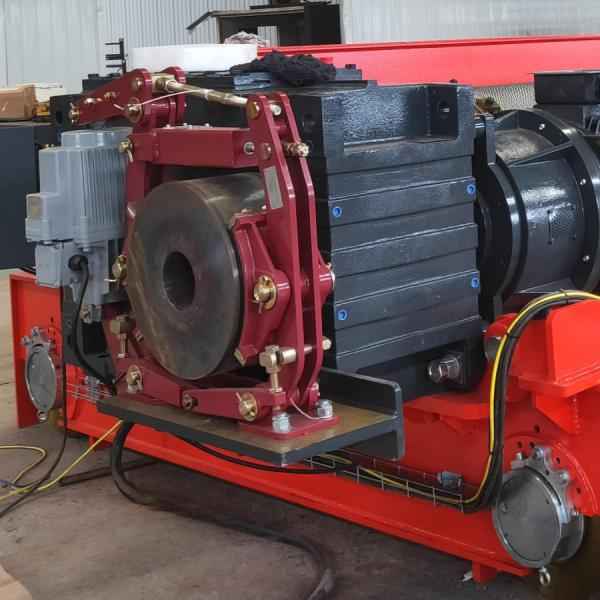
Safety brakes are crucial in crane applications, ensuring the stability and safety of the crane in case of malfunctions or accidents. Cranes are heavy-duty machines that carry significant loads, and during their operation, they are exposed to various risks. Therefore, the design and application of safety brakes are key to protecting both operators and equipment.
Main Areas of Application:
- Preventing Load Descend:
During lifting operations, if the crane’s power system fails (such as a power outage or hydraulic failure), the safety brake automatically engage to prevent the load from descending or falling. This is especially important when lifting heavy objects at high altitudes. - Protecting the Crane’s Motor and Gearbox:
The crane’s motor and gearbox endure heavy loads during operation. When an emergency occurs, safety brakes cut off power and brake the system in time, preventing damage to these critical components. - Preventing Free Fall:
In certain types of cranes (e.g., tower cranes, gantry cranes), if there is a power failure or mechanical fault, safety brake can prevent the hook or boom from suddenly falling, thus avoiding potential accidents and property damage. - Overload Protection:
Safety brakes are also designed to be linked with the crane’s load sensors. When the crane exceeds its rated load capacity, the brakes automatically activate, preventing the lifting of overloaded items.
safety brakes Operating Principles:
Safety brake typically use mechanical, hydraulic, or electromagnetic braking systems. Common modes of operation include:
- Electromagnetic Safety Brake: These use electromagnetic force to apply the brake. They are often activated automatically when the power supply is cut off.
- Mechanical Brake: These work through physical contact or friction to stop the crane, commonly seen in traditional cranes.
- Hydraulic Brake: These use hydraulic pressure to control braking, suitable for heavy-load crane systems.
Overall, safety brake are an indispensable part of the crane system. They ensure the crane remains stable in case of a malfunction, effectively preventing accidents.